Theoretical Framework
27 September
L.O. to apply the theoretical framework to media texts
Media Language
All the different elements used to construct any media product. This covers terms used, how texts are constructed and the messages conveyed. It includes; camerawork ( cinematography ), soundtrack, mise-en-scene, editing.
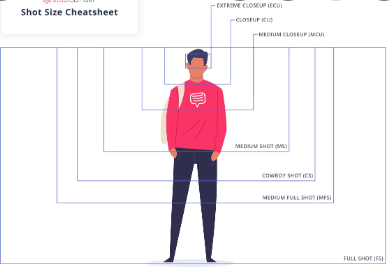
Establishing shot - you often see establishing shots at the start of a new scene or the start of the film, because it gives us information about where the scene is or what is going on, what time of day it is etc. Wide shot - the wide shot appears when you want the audience to see the position of the characters. You want to show the relationship between the subject and its environment by using the wide shot. Medium / mid shot - a neutral shot neither too close or too far away. To display what is going on with the subject. To show us waist up shots, and focus on body language and emotion. Medium close up shot ( mcu ) - reducing distraction from the rest of the environment, and to capture reactions or emotions of subject. Usually chest- up of a character. Close up shot - highlighting detail they want us to notice, very dramatic, focuses on the subjects face. Extreme close up shot - iscolating a specific area for us to pay attention to, usually the eyes, to show specific focus on a certain body part, facial feature and emotion.
Soundtrack
Includes all sound heard in a film / TV show: music, sound effects, dialogue, voiceover. Can be DIEGETIC or NON DIEGETIC. DIEGETIC : diegetic sounds are background noises that you can hear / would hear in real life. NON-DIEGETIC : any sounds that are added on after / not real in real life. if i was in the scene i would not hear the non-diegetic noises because they havent been added or dont exist yet.
29 September
Mise-en-scene
Mise-en-scene is the arrangement of the props, scenery etc on a stage of a theoretical production set. It includes everything that can be seen in a frame: costumes, props, hair, background, makeup, lighting, positioning, body language and facial expression and more.
In the stranger things poster we can look at everybody's facial expressions and it is made obvious to us that they don't look particuarly happy, but more scared,worried or serious. The darkness of the background can suggest some mystery to us, as well as the person with the odd full-body suit in the bottom right corner. The bikes the children are on dont look particuarly modern like the ones we would use now days; could this tell us this was maybe set in a different time and less modern. There is also a man with a walkie-talkie and less ordinary clothes, maybe a police uniform? Police being in the scene could suggest mystery or crime, or maybe something has gone wrong.
Just looking at this poster would personally connote to me that maybe it was set in an older time based upon the way not only the way the man in the centre of the shot is dressed, but the people behind him are all dressed in a way we wouldn't typically see so much in the modern day. For example all the men are wearing very specific hats we would usually see in an older time. The angle and way the man is positioned in the frame connotes maybe he is the main character because he is in the centre of the shot so we are focusing on him. If we look closer you can see a ferris-wheel in the background of the shot, looking a bit old and rustic, also connoting to us maybe this film is a bit older / set in an older time.
Editing
transitions, pace and speed of cuts, CGI (computer generated imagery), green screening, graphics.
Straight cut- going straight from one cut into another (pretty standard) Jump cut - to give the impression that time is passing quicker, to cute out certain bits. Cross cutting / paralell editing - way to build suspence, allows you to tell two stories at once. cut between two different things happening at the same time. crossing between two different situations Cutaway - similar to cross cutting, imforming the viewer of your environment and giving the viewer a better understanding of whats happening/ where you are in the scene Montage - a lot of clips put together from different times to show time passing/ memories happening, types of scenes where people are getting ready or waiting / thinking about something Match cuts - matching a characters motion from one scene into another. Tracking- when the camera follows the character.
4 October
Media Institutions
Media Representation











Comments
Post a Comment